Cancer
Non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma: Causes, symptoms, and treatment
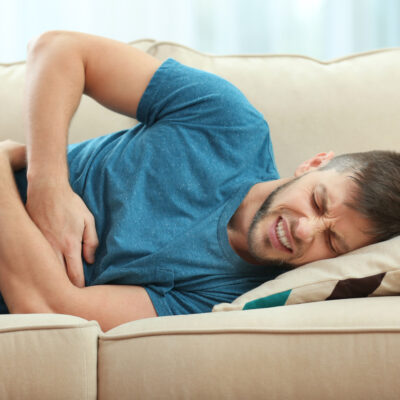
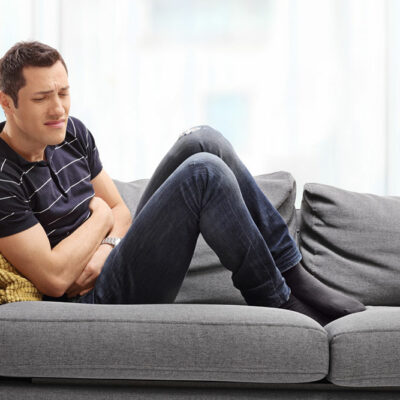
Non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma, also known as NHL, is cancer in the lymphatic system. The lymphatic system is an important part of the immune system and comprises of lymphatic vessels that carry lymph to the heart. When tumors occur in lymphocytes, a type of white blood cells, it can lead to NHL. Cancers that originate in lymph tissue are considered lymphomas. There are different types of lymphomas. A majority of NHL is categorized as B-cell or T-cell lymphoma. The common types of B-cell lymphoma are large B-cell lymphoma and follicular lymphoma. The other types of lymphoma are Burkitt’s lymphoma, marginal zone B-cell lymphoma, and extranodal marginal zone B-cell lymphoma. Causes and symptoms of non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma Physicians and researchers have not yet detected the exact cause of NHL. However, it has been found out that NHL is caused when the body produces too many abnormal lymphocyte cells that continue to grow and divide. Other medical conditions that increase the risk of this disease is an immune disorder, inflammatory bowel disease, genetic syndromes, psoriasis, family history of lymphoma, and Celiac disease. Different bacteria and viruses also increase the risk of such disease. The common symptoms of NHL are pain or swelling in the abdominal region, swollen lymph nodes, difficulty in breathing, chest pain and coughing, fatigue, weight loss, and fever.
Read More